In the past two weeks I set up a new VPS, and I run a small experiment. I share the results for those who are curious.
Consider that this is a backup server only, meaning that there is no outgoing traffic unless a backup is actually to be recovered, or as we will see, because of sshd.
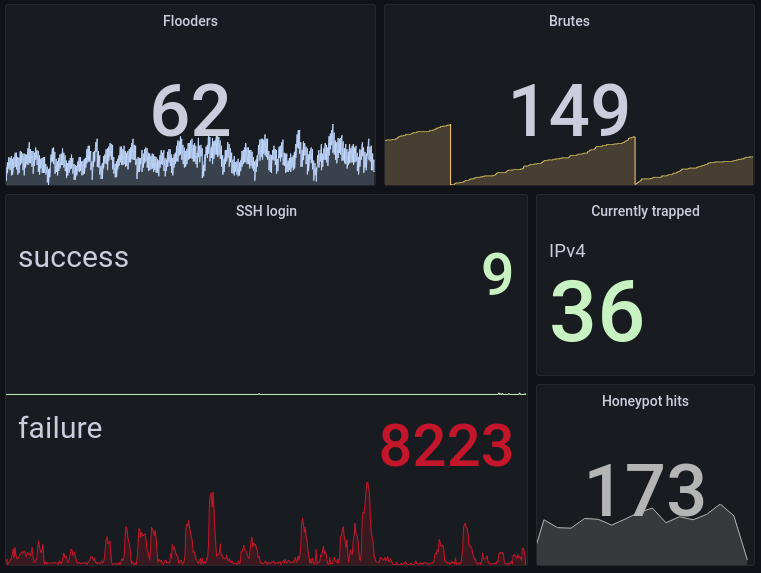
I initially left the standard “port 22 open to the world” for 4-5 days, I then moved sshd to a different port (still open to the whole world), and finally I closed everything and turned on tailscale. You find a visualization of the resulting egress traffic in the image. Different colors are different areas of the world. Ignore the orange spikes which were my own ssh connections to set up stuff.
Main points:
-
there were about 10 Mb of egress per day due just to sshd answering to scanners. Not to mention the cluttering of access logs.
-
moving to a non standard port is reasonably sufficient to avoid traffic and log cluttering even without IP restrictions
-
Tailscale causes a bit of traffic, negligible of course, but continuous.
Acronyms, initialisms, abbreviations, contractions, and other phrases which expand to something larger, that I’ve seen in this thread:
Fewer Letters More Letters DNS Domain Name Service/System HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol, the Web IP Internet Protocol SSH Secure Shell for remote terminal access UDP User Datagram Protocol, for real-time communications VPN Virtual Private Network VPS Virtual Private Server (opposed to shared hosting) nginx Popular HTTP server
7 acronyms in this thread; the most compressed thread commented on today has 8 acronyms.
[Thread #42 for this sub, first seen 14th Aug 2023, 15:55] [FAQ] [Full list] [Contact] [Source code]
Good bot!
Great bot
Public key auth, and fail2ban on an extremely strict mode with scaling bantime works well enough for me to leave 22 open.
Fail2ban will ban people for even checking if the port is open.
Honest question, is there a good default config available somewhere or is what
apt install fail2bandoes good to go? All the tutorials I’ve found have left it to the reader to configure their own rules.Yeah fail2ban has worked great for me
If Fail2Ban is so important, why the h*** does it not come installed and enabled as standard?!
Security is the number-1 priority for any OS, and yet stock SSHD apparently does not have Fail2Ban-level security built in. My conclusion is that Fail2Ban cannot therefore be that vital.
I get what you say, and you’re definitely not wrong to do it. But as I see it, you only saved ~80Kib of ingress and a few lines of logs in the end. From my monitoring I get ~5000 failed auth per day, which account for less than 1Mbps average bandwidth for the day.
It’s not like it’s consuming my 1Gbps bandwidth or threatening me as I enforce ssh key login. I like to keep things simple, and ssh on port 22 over internet makes it easy to access my boxes from anywhere.
I don’t get why people leave interfaces the public doesn’t need access to open to the public – especially SSH.
Use a VPN if you need access to those interfaces from the “outside”. They’re stupidly easy to set up these days, particularly with Wireguard.
A VPN is easy to setup (and I have it setup by the way), but no VPN is even easier. SSH by itself is sufficiently secure if you keep it up to date with a sane configuration. Bots poking at my ssh port is not something that bother me at all, and not part of any attack vector I want to be secure against.
Out of all the services I expose to the clear web, SSH is probably the one I trust the most.
I would generally agree with this a strong password and SSH without keys has never gone sideways for me and over 15 years of having public Linux servers. but I also make sure to install all security updates on a regular basis on any server no matter what SSH configuration is.
Agreed ! Also it would make graphs pretty boring ;)
Defense in depth – maybe I’m paranoid, but just because something is unlikely doesn’t mean an extra layer of security isn’t advantageous. Particularly when I already have a VPN, so there’s little reason not to use it.
Plus, my logs are easily checked as a side effect.
To each their own ! Security is a complex topic which usually resolves to adjusting the “security/annoyance” cursor to the best position.
In my case the constraints of using a VPN simply outweighs the security benefits.
ssh -p 12345 would leave your boxes accessible from anywhere too. Other blocks of IPs receive 10 times or more requests, as scanners can focus on blocks of ips from major providers.
Yeah I know, I just don’t really care about that traffic to bother changing it :) Also, I’m talking about a server hosted on Hetzner, so I feel like it’s scanned a lot.
You really shouldn’t have something kike SSHD open to the world, that’s just an unnecessary atrack surface. Instead, run a VPN on the server (or even one for a network if you have several servers on one subnet), connect to that then ssh to your server. The advantage is that a well setup VPN simply won’t respond to an invalid connection, and to an attacker, looks just like the firewall dropping the packet. Wireguard is good for this, and easy to configure. OpenVPN is pretty solid too.
You say this and are downvoted.
While we are coming off the tail of Def Con where there where a plethora or small talks and live examples of taking advantage and abusing just this.
Just trying to parse your comment, I assume your first “this” and second “this” are referring to different things, right?
I don’t understand your comment, what you are saying. Could you elaborate a bit, please? I’m interested why it’s a bad idea what previous comment suggested.
Of course I can dig into DefCon videos and probably would do if needed, but perhaps you know what exactly the issue is
The first this means the comment he answered to and the second one means ssh being used as an attack surface, being described in defCon talks
Or, you know, just use key auth only and fail2ban. Putting sshd behind another port only buys you a little time.
I’ve noticed that a lot of the scans these days almost always switch IPs after 2-3 attempts, making IP blocking a lot more difficult.
Let’s say that you could ban for an indefinitely large amount of time after a single failure to authenticate, that’d make them run out of IPs much quicker than you’d run out of CPU/BW, so I don’t really see the issue
Potentially yeah, although a single failure means I might lock myself out by accident.
True, but very unlikely (once your ssh client is configured once and for all), and in that event you can always switch connection (use a data network, proxy, vpn, hop from another server you have ssh access, etc)
Yeah but the majority of bots out there are going after easy prey. Honestly, if you use public key authentication with ssh you should be fine, even if it is on port 22. But it does of course clog up access logs.
The majority of bots out there are stopped by just using a hard to guess password. It’s not them that you should be worried about.
The majority of bots doesn’t even show up in the logs if you disable password auth in the server config, as you typically should.
And yet it is more likely that tailscale get owned since the reward is much higher. I take my chances with my secured openssh server at port 22 vs a 3rd party company who controlls the access.
Just setup a wireguard system that’s pretty bulletproof
So is SSH
Wireguard doesn’t respond but I agree open-ssh is pretty solid. Can’t speak for any of the other ssh implementations. It can also be poorly configured. Like you could use a password
The benefit of Wireguard is that if you screw it up, it just won’t work. It basically enforces security.
Well, unless you tried to use the original PFSense module.
I don’t know if it was mentioned already but how could I check if my ports are under “attack”? OPs graphic looks really nice
Hi, to check attacks you should look at the logs. In this case auth.log. Being attacked on port 22 is not surprising neither really troublesome if you connect via key pair.
My graph was showing egress traffic, on any kind of server the traffic due to these attacks would have been invisible but on a backup server which has (hopefully) only ingress you can clearly see the volume of connections from attackers from bytes teansmitted
Prevent password auth and setup sshguard. Wireguard is very nice in that it doesn’t support password auth.
I don’t get tailscale? In-kernel Wireguard is easy to setup. What does it add to this?
I believe it adds a third party server to help facilitate communication between clients.
Tailscale is a nice way to set up a private network between your machines. It’s perfectly fine.
But isn’t that the most trivial application of Wireguard?
Networking two machines is easy; networking several with good onboarding and DNS is not as easy.
I think I’ve been too ignorant about Tailscale, primarily about the fact that it actually does direct peer-to-peer connections which would indeed be a pain with just Wireguard and not always trivial. I’m starting to get why so many people here are recommending it so thanks for the answer, maybe I should consider using it myself. :)
Tailscale is built on top of wireguard. It just manages all the hassle of configuring it. In my case it was a godsend as I have like 10 devices all roaming and scattered across multiple countries. It’d be a massive headache to type down IPs and whatnot every time one changes networks.
Thanks for enlightening me on that aspect, setting that up with just Wireguard would indeed be a pain or outright impissible without additional tools (e.g. for UDP hole-punching), maybe I should also consider it :)
I think it’s just the ease of GUI for people. This isn’t to shit on anyone, btw. A lot of people don’t like dealing with the keys and IPs involved, few as there may be, with setting up wireguard.
If someone else has a compelling difference or reason to use tailscale then I’d be happy to hear it. I tried it once and it worked fine enough. But wireguard works just as fine and takes the same time to setup if you already know what to do. Like wireguard seriously takes 2 minutes.
I’m not using Tailscale, but I’d imagine that if you wanted to form a private network that involves devices controlled by non-technical people, the GUI becomes less of a “don’t like to deal with keys/IPs” and more of a “can’t deal”.
I’ll take that tiny amount of traffic telling scanners there’s no password auth over having to remember port settings for ssh, scp and rsync any day.
My configs remember stuff for me.
vim ~/.ssh/configYeah, but how do you close VIM then? Restarting the computer takes some time!!!111
Checkmate!!
For me it’s not about the traffic, more the log spam.
Generally I’ll have :22 enabled internally, and anything non-standard is defined in
~/.ssh/configand shared out so I don’t have to remember things.Fair point. These logs are only useless chatter anyway for everyone with proper key auth.
I am not in IT, what does this mean ?
Computers communicate across networks using ports. Port 22 is a commonly used remote administration port called ssh. Bots go around probing computers with an open port 22 hoping to find badly secured or outside misconfigured ssh servers to turn them into bots and crypto miners, etc.
Just do it properly and configure sshd securely. When you have a machine exposed to the internet, you should expect it to be attacked. If you really want to give the finger to bots, run endlessh on port 22 and keep sshd on a non-standard port. Stay safe.
endlessh
Lmao thanks for this
I opened a raw text channel on the Telnet port for a personal game engine project and someone tried to enable commands and do some shady stuff. Unfortunately for them, that’s not a valid chess move.
Whys this a problem disable password auth and wish em good luck lol.
As others have already said, set up a VPN like wireguard, connect to the VPN and then SSH to the server. No need to open ports for SSH.
I do have port 22 open on my network, but it’s forwarded to an SSH tarpit: https://github.com/skeeto/endlessh



















